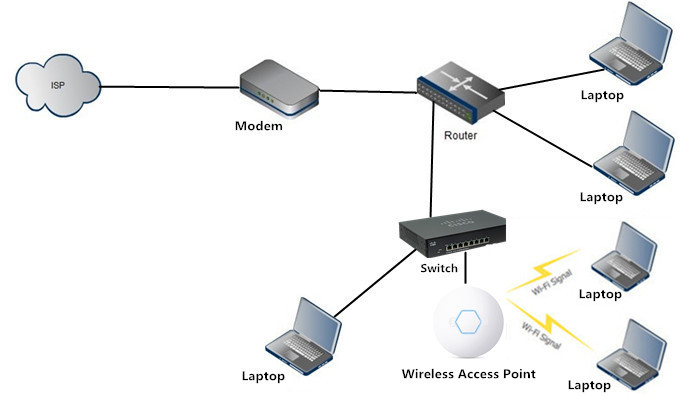
Network latency is a term used to describe the time delay that occurs while data is being transmitted from one point to another through a network. It can be caused by various factors such as limited bandwidth, processing delays and distance between the communicating parties. In computer networks, latency is measured in milliseconds (ms) and is a critical factor when it comes to network performance.
High network latency can result in slow response times, delays in video or audio transmissions, and interruptions in the communication between the client and server. For applications that rely on real-time data exchange, such as online gaming or video conferencing, network latency plays a crucial role in delivering a seamless experience to the user.
To reduce network latency, several methods such as data compression, caching, and load balancing are used. These techniques help to improve network performance by reducing the size of the data being transmitted and distributing the workload amongst multiple servers. Additionally, services like Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are commonly used to reduce network latency by caching data closer to the end-user, thus reducing the round-trip time.
It is important to note that different network types have different levels of latency. For instance, satellite communications tend to have higher latencies due to the distance that signals need to travel, while fiber optic cables have lower latencies as signals travel at the speed of light.
In conclusion, network latency is a critical factor when it comes to network performance. Reducing latency is essential for applications that require real-time data exchange, and several techniques can be used to achieve this. By understanding the factors that cause network latency, one can take steps to optimize their network infrastructure and ensure a seamless user experience.