LAN to WAN: Understanding How It Works
When it comes to networking, the terms Local Area Network (LAN) and Wide Area Network (WAN) are frequently used. To put it simply, a LAN is a network of computers and devices that are connected within a small geographical area, such as an office, school, or home. On the other hand, a WAN connects multiple LANs over a larger geographical area, such as a city, country, or even the entire world.
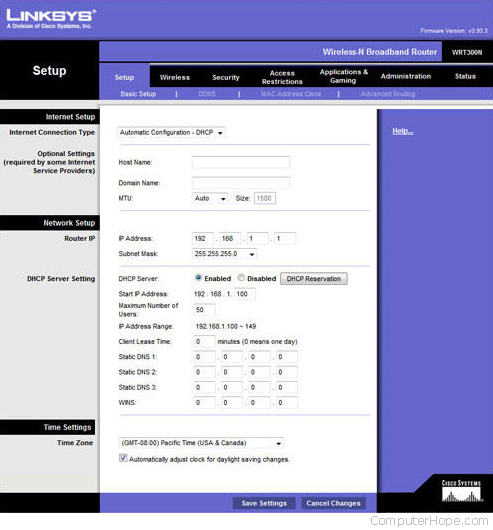
To connect a LAN to a WAN, a router is usually required. A router is a networking device that forwards data packets between computer networks. It connects a LAN to the internet or another WAN. The router acts as a gateway for the devices on the LAN to access the resources on the WAN.
One of the crucial things to keep in mind while configuring a LAN to WAN connection is the IP addressing scheme. Each device on a network has a unique IP address that identifies it on the network. Properly configuring the IP addresses is important, as it determines the network addressing and routing.
Another important consideration is the security of the LAN, as connecting to a WAN can potentially expose the LAN to various security threats. Using firewalls or other security measures can help protect the network from unauthorized access and attacks.
In conclusion, connecting a LAN to a WAN requires a router and proper configuration of IP addresses, network addressing and security. It is critical to ensure that the connection is secure and properly configured, to reduce the risk of potential security threats on the network.