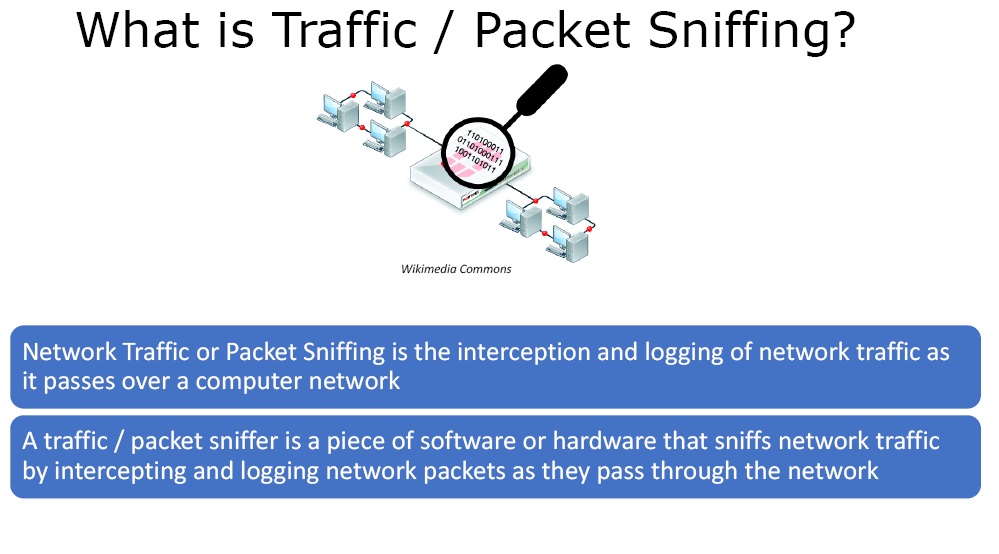
Router VPN setup
A virtual private network (VPN) is a network that encrypts and protects your internet connection, providing a secure and private browsing experience. While setting up a VPN on a device such as a laptop or mobile phone is relatively easy, setting up a VPN on a router can extend the benefits of the VPN to all devices connected to the router.
To set up a VPN on a router, first, you need to select a VPN provider that supports router configurations. Then, you need to configure the router to use the VPN provider's server.
The first step is to log in to your router's interface. The interface can be accessed through the router's IP address, which can be found on the bottom or back of the router or through the router's documentation. Once logged in, navigate to the router's VPN settings.
In the VPN settings, you will need to configure the VPN connection using the VPN provider's server information, such as the server address, username, and password. You may also need to choose the VPN protocol and port number.
After configuring the VPN connection, you will need to set up the VPN client on each device you want to use with the VPN. Alternatively, some routers come with built-in VPN clients, enabling you to connect to the VPN directly from the device without the need for additional software.
Once the VPN setup process is completed, you can enjoy the benefits of a secured network, including browsing the internet privately, securely, and with anonymity. Setting up a router VPN may seem complicated, but it is a relatively simple process that can be completed with a little bit of knowledge and research.