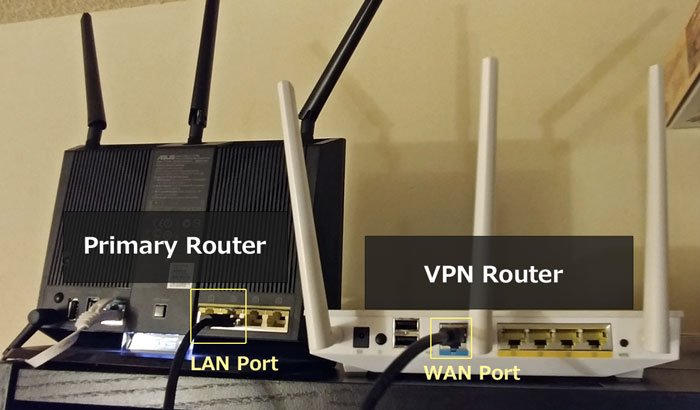
Wireless transmission power is an essential aspect of modern communication technology. It refers to the amount of energy that is required to transmit a wireless signal from one point to another. The power is measured in watts and is an important factor in the range and reliability of a wireless network.
The strength of the wireless transmission power determines the coverage area of the wireless signal. The higher the transmission power, the greater the range the signal can travel. This is important in outdoor wireless applications where the signal needs to reach a wide area.
Wireless transmission power is also critical in indoor wireless networks. The power output of a wireless access point must be high enough to provide coverage throughout a building or large room, but not so high that it causes interference with neighboring wireless networks.
Wireless devices also have a power output, which determines how far they can communicate with an access point. The greater the device's power output, the farther it can communicate, increasing the range of the wireless network.
However, high transmitter power can lead to negative effects, such as disruption of other wireless transmissions, electromagnetic interference, and increased power consumption. It is, therefore, essential to balance the power with other factors to ensure optimum performance of the wireless network.
Moreover, wireless transmission power is regulated by national and international authorities to control its potential impact on human health and the environment. These regulations specify the maximum power limits that wireless networks and devices can produce.
In conclusion, wireless transmission power is a crucial aspect of wireless communication technology. It determines the range, reliability, and performance of wireless networks and devices. However, excessive power can lead to unwanted effects, and therefore, it is essential to manage power levels carefully to avoid interference and comply with regulations.