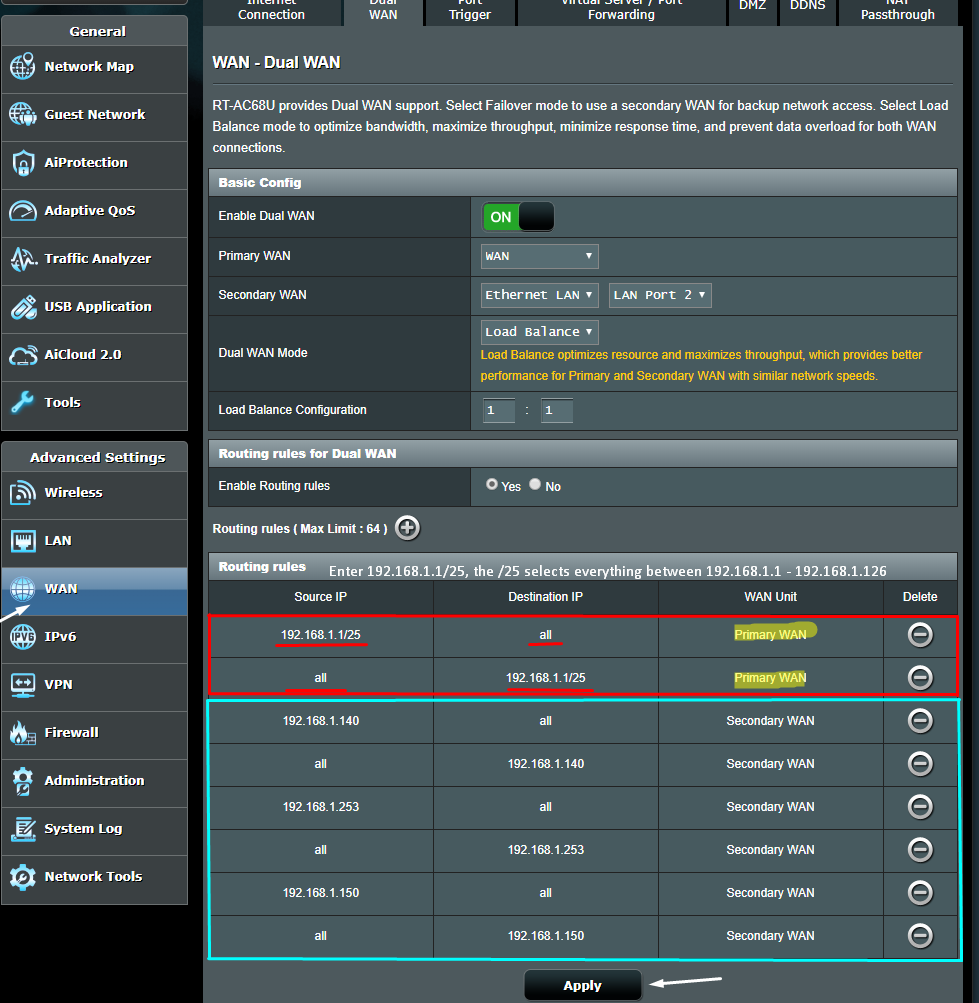
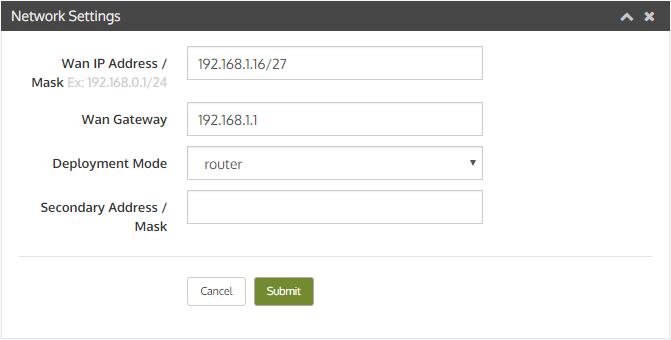
Static IP Setup
Setting up a network requires assigning IP addresses to each device. A static IP address is a permanent address assigned to a computer or device to keep it recognizable in the network. This setup ensures the device always has the same IP address, even if it reboots or changes location.
Compared to dynamic IP addresses, which are assigned automatically by a DHCP server each time a device connects to the network, static IP addresses are manually configured. This option is best for servers or devices that need a permanent IP address assigned to them.
Here are the steps to set up a static IP address on Windows computers:
1. Open the Control Panel and navigate to Network and Sharing Center.
2. Click on Change adapter settings and select the network adapter you want to assign a static IP address to.
3. Right-click on it and click on Properties.
4. Highlight Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4) and click Properties.
5. Under the General tab, select Use the following IP address and enter the IP address, subnet mask, default gateway, and DNS server information.
6. Click OK to save the changes.
Setting up a static IP address on other devices, such as routers, switches, or Linux computers, might have different procedures.
In conclusion, static IP addresses provide for consistent and stable connectivity for specific devices in a network. Setting it up is easy and can be handled manually based on the device or computer’s configuration. It makes it easy if you want to create a permanent connection with servers or have a device that requires continuous access in the network.