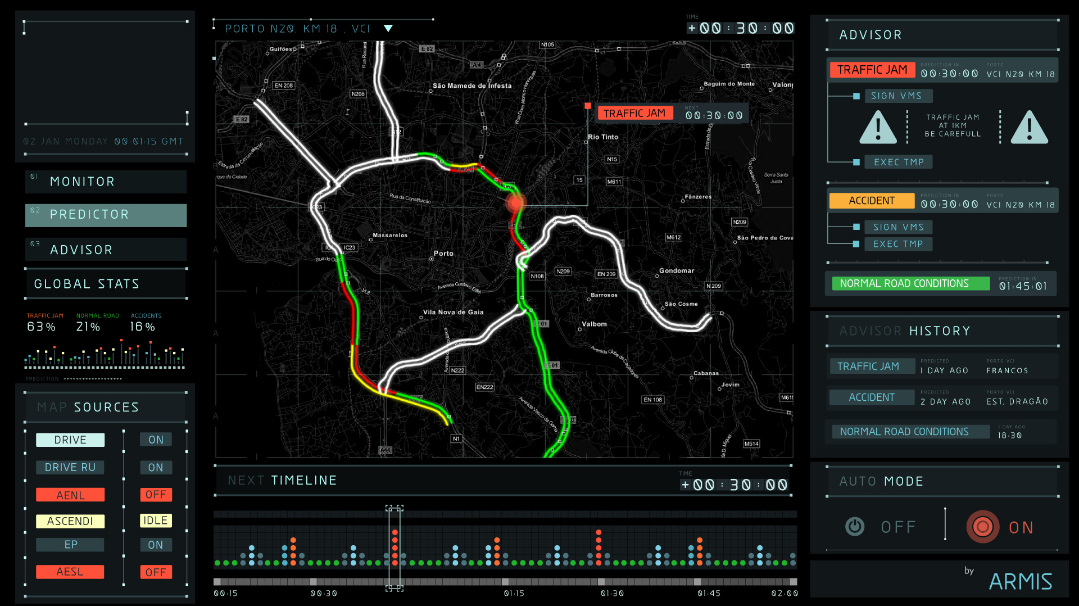
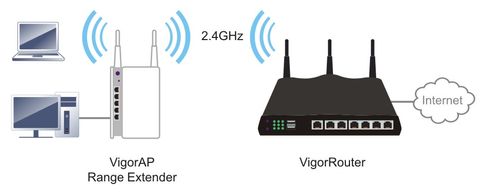
Router Port Testing Explained
Router port testing is an essential component of network security testing. It involves checking each port of a router to ensure that it is properly configured and secure against unauthorized access. By conducting router port testing, network administrators can proactively identify any vulnerabilities in the network and implement measures to mitigate the risks.
One of the primary reasons for router port testing is to identify potential security loopholes in the network. For instance, open ports can be used by hackers to launch attacks on the network, steal valuable data or plant malware. As such, it is vital for network administrators to ensure that all ports are closed unless explicitly required for critical services.
Router port testing also involves validating the accessibility of network services hosted on the router. Some services are essential for network operations, such as FTP, HTTP, SNMP, and SSH. However, if these services are not properly configured, attackers may take advantage of them to compromise the network. Router port testing helps to ensure that all services are correctly configured and only accessible by authorized users.
Moreover, router port testing is necessary to ensure that the router is functioning correctly and efficiently. A faulty router may result in network outages, data loss, and reduced productivity. By conducting regular port testing, network administrators can detect any performance issues and resolve them before they escalate.
In summary, router port testing is an essential part of network security, and it ensures that routers are configured correctly and securely. It helps identify and mitigate vulnerabilities that attackers may use to compromise the network. Network administrators should regularly conduct port testing to ensure network performance, availability, and security.